Open clusters, loose collections of young stars in galaxies, have not received much attention in the MOND literature as of yet. This is mostly because high quality data on these structures has not been available. Last year Hunt et al. published a giant catalog of open clusters based on Gaia DR3 data with accurate distances and astrometric parameters. This catalog was expanded on a year later by the same team to include completeness-corrected photometric masses. The mass functions of these clusters are compatible with the Kroupa IMF.
This open cluster catalog can be compared to Milgrom’s Law (also known as the radial acceleration relation, RAR) which is the primary prediction of Milgromian dynamics. For this we need the observed acceleration and the baryonic acceleration. The observed acceleration can be calculated as gobs=3σ*2/R. Here σ* is the average one dimensional velocity dispersion estimated from the two transverse velocities and the radial velocity, weighted by the number of observations for each. This assumes that the velocity dispersion is the same in each spatial dimension. The baryonic acceleration is gbar=GM/R2. Therefore we can create the following plot:
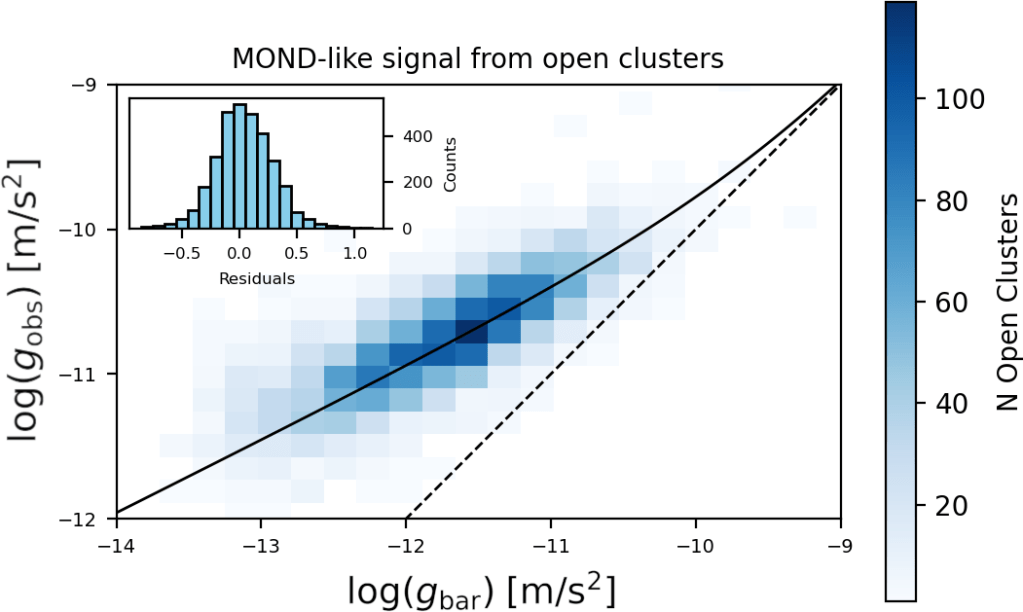
Edit: An earlier version of this plot showed large scatter due to the inclusion of highly unreliable radial velocities in the velocity dispersion leading to the erroneous conclusion that most open clustes (and nearly all moving groups as classified as such by Hunt et al.) are not in virial equilibrium.
The plot only based on the precise proper motions shows that open clusters follow the RAR. That solid black line was first posited in 1983 and it just pops up in the data four decades later. Open clusters must happen to reside in those parts of the galaxy where the external field is negligible due to local matter distribution causing a pocket of space where the gravitational field is very small. Otherwise this result is impossible due to the external field effect.
Further research into open clusters suggest that in systems were an appreciable external gravitational field is present this is observable due to asymmetries in the tidal tails of the clusters which should be symmetrical in Newtonian mechanics. See this paper and the two graphs below.





Leave a Reply